Select your cluster, then go to Configure>vSAN>Services. Click “Configure vSAN”.
You’ll need to choose the type of vSAN cluster to configure:
1) Single Site Cluster (with or without custom fault domains)
2) Two-node Cluster
3) Stretched Cluster
4) HCI Mesh Compute Cluster
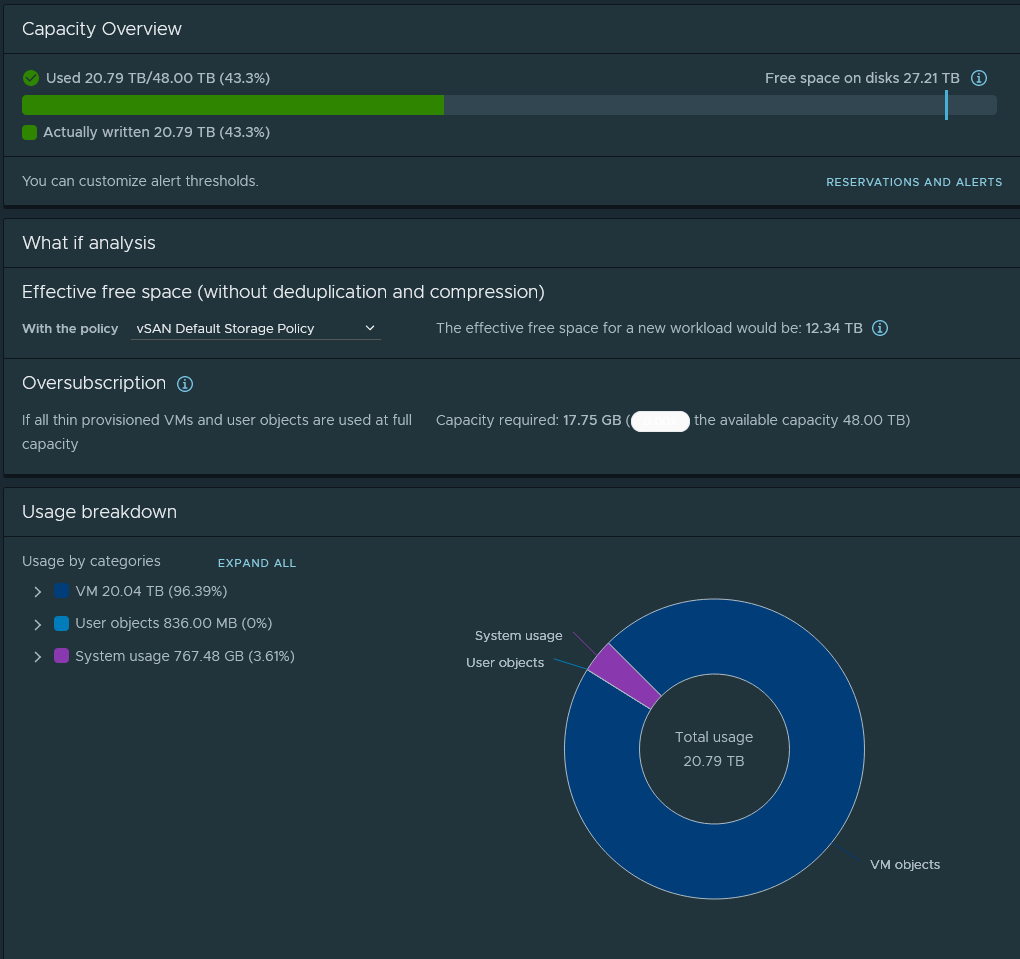
All of these choices affect the redundancy and capacity of your datastore, something we’ll cover later in this chapter.
I chose to use a Single-site cluster with custom fault domains.
For my 3-node cluster, I create 3 domains, one containing each host. My configuration allows for one host failure to be tolerated by vSAN.
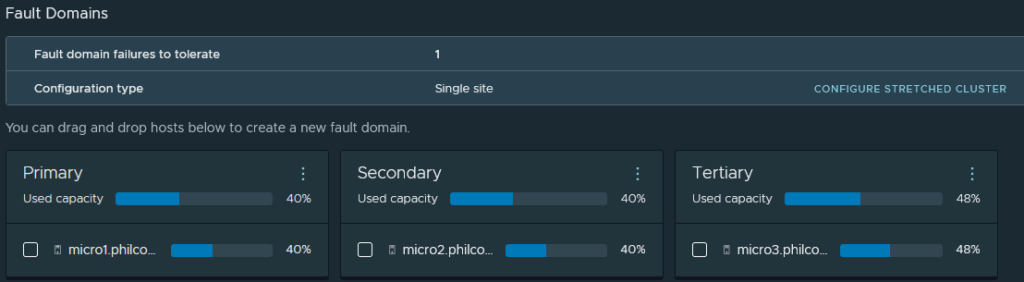
The Fault Domains have an impact on the amount of storage available. The more failures you set up your vSAN instance to tolerate, the more storage it will reserve for redundancy (and you’ll end up with less total storage on your vSAN datastore as a result).
Conversely, if you set up your vSAN configuration to allow for the maximum storage possible, this will leave you with reduced redundancy in the event of a failure.
Then click “Next” to choose the vSAN services to use. In this lab instance I’m just using basic vSAN datastores, none of the additional services.
Claim disks for capacity and cache for each of the hosts that are going to provide vSAN resources. Each host needs at least one flash device, and at least one capacity device.
In my case, I add the 256Gb SSD as cache, and the 18TB of disks as capacity for each host.
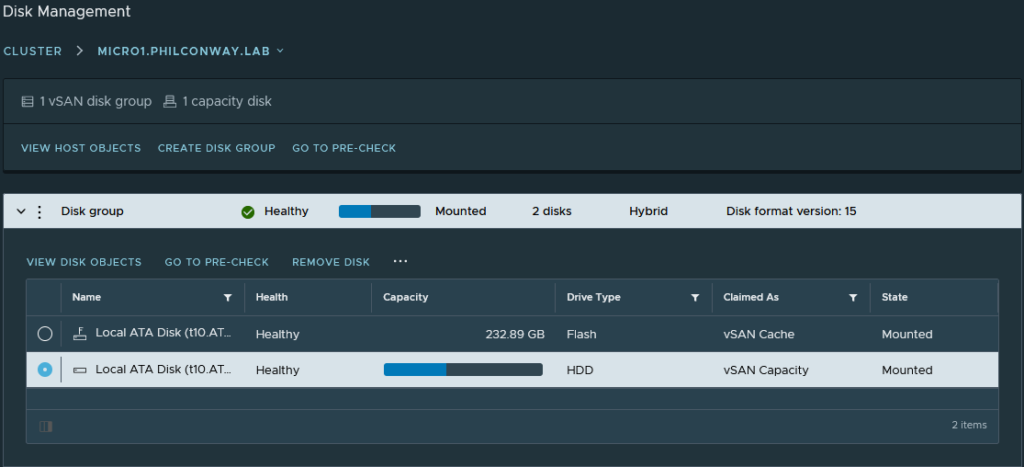
Review the configuration and click Finish.
With Disks allocated and Fault Domains configured, you should end up with a vSAN datastore for your cluster.